
eDiscovery forensics: Bridging legal review and digital evidence
Introduction
The intersection of eDiscovery and digital forensics is increasingly vital to modern legal investigations. As business data spreads across the cloud, numerous endpoints, and remote work environments, legal teams must not only identify relevant evidence but also prove its authenticity, preserve its integrity, and prepare it for court.
For the purposes of this blog, we will refer to this intersection as “eDiscovery forensics.” While “eDiscovery forensics” isn’t a formal industry term, it reflects the growing overlap between digital forensics and eDiscovery as organizations fuse the legal requirements of eDiscovery with the investigative rigor of digital forensics
What is eDiscovery?
Electronic Discovery, also known as eDiscovery, is the process of collecting, reviewing, and exchanging electronically stored information for use as evidence in legal cases. According to cdslegal.com, eDiscovery entails applying legal requirements to ensure that electronically stored information is identified, preserved, and produced in a way that meets the standards for admissibility and defensibility in court. By incorporating the investigative rigor of digital forensics, eDiscovery practices help ensure that all electronically stored information, whether emails, documents, or data from complex systems, is complete, properly handled, and ready to withstand legal scrutiny
This includes emails, files, chat logs, social media data, and much more. The process is governed by the Electronic Discovery Reference Model (EDRM), a framework that guides organizations through nine repeatable steps from information governance through to presentation in court.
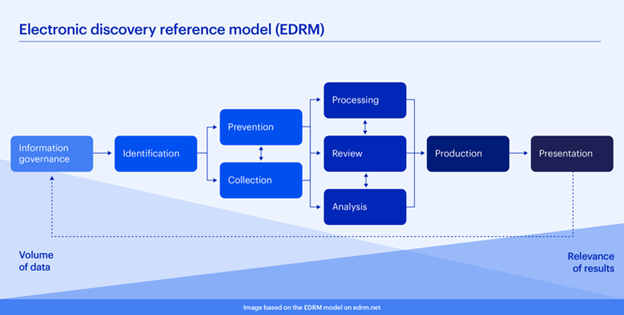
Traditional eDiscovery solutions are highly effective and comprehensive for legal review workflows. However, as digital evidence becomes more fragmented and distributed across cloud platforms, mobile devices, virtual machines, and remote endpoints, they may not offer the same level of completeness in data collection capabilities as specialized digital forensics tools, particularly when it comes to recovering deleted, hidden, or system-level artifacts.
Why digital forensics matters in eDiscovery
Digital forensics is the science and methodology of identifying, preserving, and analyzing digital evidence when that evidence is hidden, deleted, encrypted, or otherwise inaccessible to ordinary users or software. Forensic tools and specialists can recover deleted files, analyze metadata, reconstruct timelines, and prove that evidence hasn’t been altered, capabilities that standard eDiscovery platforms alone can’t offer.
Forensic collections go far beyond the “user-visible” layer, surfacing critical evidence that would otherwise be missed.
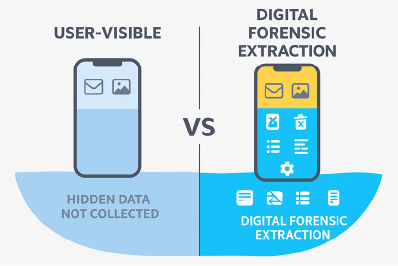
How digital forensics and eDiscovery are different
- eDiscovery solutions are typically focused on collecting, processing, reviewing, and producing already accessible data (inboxes, file shares, and cloud accounts).
- Digital forensics specializes in deep analysis, recovering deleted or hidden artifacts, validating data integrity, and building a defensible chain of custody.
How they work together
In complex cases such as fraud, data exfiltration, or insider threats, digital forensics supports eDiscovery by surfacing hidden evidence, ensuring data authenticity, and preserving metadata critical for judicial review.
Complex data challenges in eDiscovery forensics
Modern investigations face hurdles that only a fusion of eDiscovery and forensics can overcome:
- Geographically dispersed workforces (remote/hybrid work)
- Fragmented data across endpoints, mobile, and multiple clouds
- High data volume and variety
- Strict chain of custody requirements
- Timeliness—rapid collections and reviews
- Need to avoid over- or under-collection
- Privacy and legal compliance

The benefits of eDiscovery forensics
eDiscovery forensics enhances legal defensibility and reduces risk:
- Recovers deleted or hidden data not accessible to standard tools
- Documents provenance (where the data came from and who touched it)
- Builds reliable timelines using metadata, logs, and system artifacts
- Reduces the risk of sanctions or spoliation by maintaining integrity
- Enables focused collections, avoiding costly over-collection
Forensic tools like Magnet Axiom Cyber and Magnet Nexus allow teams to extract, parse, and analyze all relevant data. Delivering a more complete and defensible data set to the legal review stage.
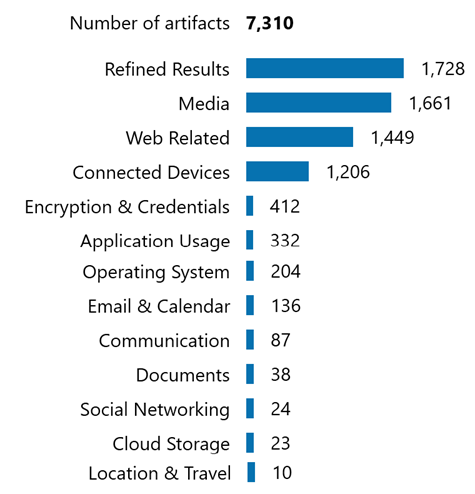
Digital forensic artifacts relevant to eDiscovery
Digital forensic software can collect and analyze artifacts including:
- Deleted files and folders (not visible to user or standard eDiscovery:
Deleted data can provide crucial evidence, such as attempts to hide or destroy information. Recovering these files ensures that potentially relevant evidence isn’t overlooked simply because it was intentionally or accidentally deleted. This data could be directly relevant to the request for service. - File system metadata (creation, modification, deletion timestamps):
Metadata provides a timeline of user and system activity, helping to establish when a file was created, altered, or removed. This is essential for building a defensible narrative and validating the authenticity of evidence in eDiscovery. - Windows Registry and system logs:
The registry and logs track a wide range of system and user actions, such as installed software, USB usage, or login events. These artifacts help investigators verify how and when data was accessed or modified, supporting a more thorough review. - Application logs and usage history:
Logs from applications can reveal communication patterns, document edits, or app usage that is relevant to the legal matter. This information helps to understand user intent and establish context for specific actions. - Shadow copies and snapshots:
Shadow copies and snapshots are backup versions of files or entire systems, often created automatically by the operating system. Accessing these can restore prior versions of important files, recovering data that would otherwise be lost. - Memory dumps (RAM analysis):
A snapshot of system memory can contain passwords, running processes, decrypted data, and live chat fragments. This volatile information is often critical for reconstructing real-time events or identifying unauthorized activity. - Network connection histories:
Records of network activity, such as Wi-Fi connections or remote access sessions, help map how devices communicated internally and externally. This can reveal unauthorized data transfers or connections that are relevant to the investigation. - Artifacts of anti-forensic activity (evidence wiping, encryption):
Traces of data wiping or encryption tools indicate potential attempts to hide or destroy evidence. Identifying these activities is important for understanding if data has been intentionally manipulated or erased. - Mobile device artifacts (full file system, including app data):
Mobile devices store a wealth of business communications, location data, and app usage details. Full file system extractions go beyond user-accessible data, uncovering deleted messages, app-specific data, and logs critical for a complete eDiscovery review.
File carving is a powerful digital forensic technique used to recover files that have been deleted or lost from the file system, even when their original directory entries are no longer available. By analyzing raw data on a storage device, forensic tools can reconstruct and extract files based on known patterns or file signatures, rather than relying on file system records. These files were completely deleted from the file system and were recovered by Axiom Cyber. Traditional eDiscovery software would not have found these files.
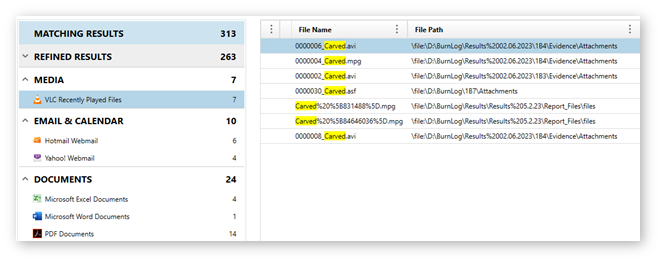
These details, to include timeline-related artifacts, are crucial for building defensible stories about “who did what, when, and how.”
Risks of confusing eDiscovery and digital forensics
Failing to distinguish between eDiscovery and digital forensics creates several pitfalls:
- Critical evidence is missed (under-collection)
- Data overload slows review (over-collection)
- Sanctions or adverse inference if evidence is lost or mishandled
A robust eDiscovery forensics workflow ensures these risks are minimized.
Best practices for integrating eDiscovery and digital forensics
- Engage forensic experts early in the case
- Define clear scope and protocols for evidence handling
- Use forensically sound tools and methods for collection and preservation
- Maintain meticulous documentation (chain of custody, acquisition logs)
- Leverage platforms like Magnet Axiom Cyber for deep collection, culling, and parsing before data enters your review stack
Magnet Forensics: Connecting eDiscovery and digital forensics
Magnet Forensics solutions bridge the gap between traditional eDiscovery and advanced digital forensics.
- Magnet Axiom Cyber: Ingests data from workstations, servers, mobile devices, cloud accounts, and cloud/virtual environments, parsing artifacts at a forensic level and allowing deep search/culling before eDiscovery production.
- Magnet Nexus: Enables remote, cloud-based collection from endpoints, streamlining collections for distributed workforces.
- Magnet Verakey: Full file system extractions from mobile devices, surfacing data missed by logical acquisitions. Verakey also offers a category extraction that can include data only from the full file system extraction. This targeted approach of category extractions offers several benefits and is especially useful when time is limited or where privacy and regulatory concerns require limiting the scope of data collection.
Logical vs. full file system extractions
Traditional eDiscovery tools usually collect data visible to the end user: documents, photos, and emails. Magnet Verakey conducts full file system extractions, capturing hidden, deleted, or system-level artifacts essential for reconstructing timelines and proving intent or data manipulation.
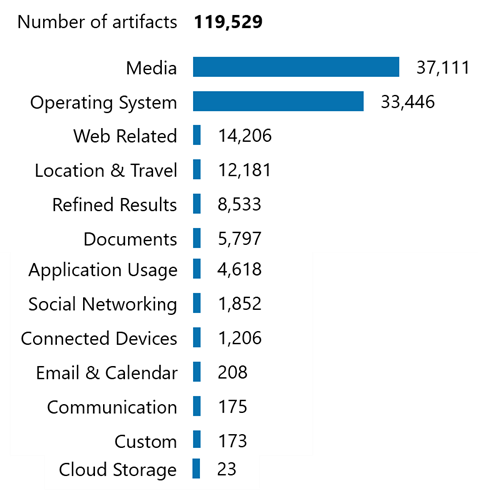
Conclusion
eDiscovery forensics is the foundation for reliable, defensible, and comprehensive legal review in today’s data-driven investigations. By blending the speed and scale of eDiscovery with the rigor and depth of digital forensics, legal and investigative teams can ensure no evidence is left behind, data integrity is maintained and can help ensure their findings will stand up in court.
Ready to learn more?
Explore how Magnet Forensics solutions can optimize your eDiscovery forensics workflow. Contact us for a demo.